LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is an advanced remote sensing technology that is transforming plantation management through its ability to deliver high-precision, three-dimensional data. By emitting laser pulses and measuring their return time, LiDAR creates accurate 3D models of landscapes and vegetation, offering powerful insights for precision agriculture.
How LiDAR Works
LiDAR functions by sending laser pulses toward the ground and measuring the time it takes for the reflected signals to return. There are two key types: Discrete Return LiDAR, which captures specific surface points, and Full-Waveform LiDAR, which records continuous data for more detailed analysis. It operates using either the Time-of-Flight (ToF) method or Phase Shift Measurement (PMS), both of which generate detailed elevation and terrain models critical for plantation planning.
Key Applications in Plantation Management
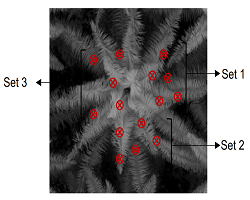
- Soil Leveling and Irrigation Planning - LiDAR-generated Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) help identify variations in terrain, making it easier for farmers to plan accurate soil leveling and water flow management. When integrated with GPS (Global Positioning System)-enabled machinery, LiDAR ensures precision grading and uniform water distribution, reducing waterlogging, runoff, and soil erosion. These models also support the design of efficient irrigation systems like contour farming and drip irrigation.
|
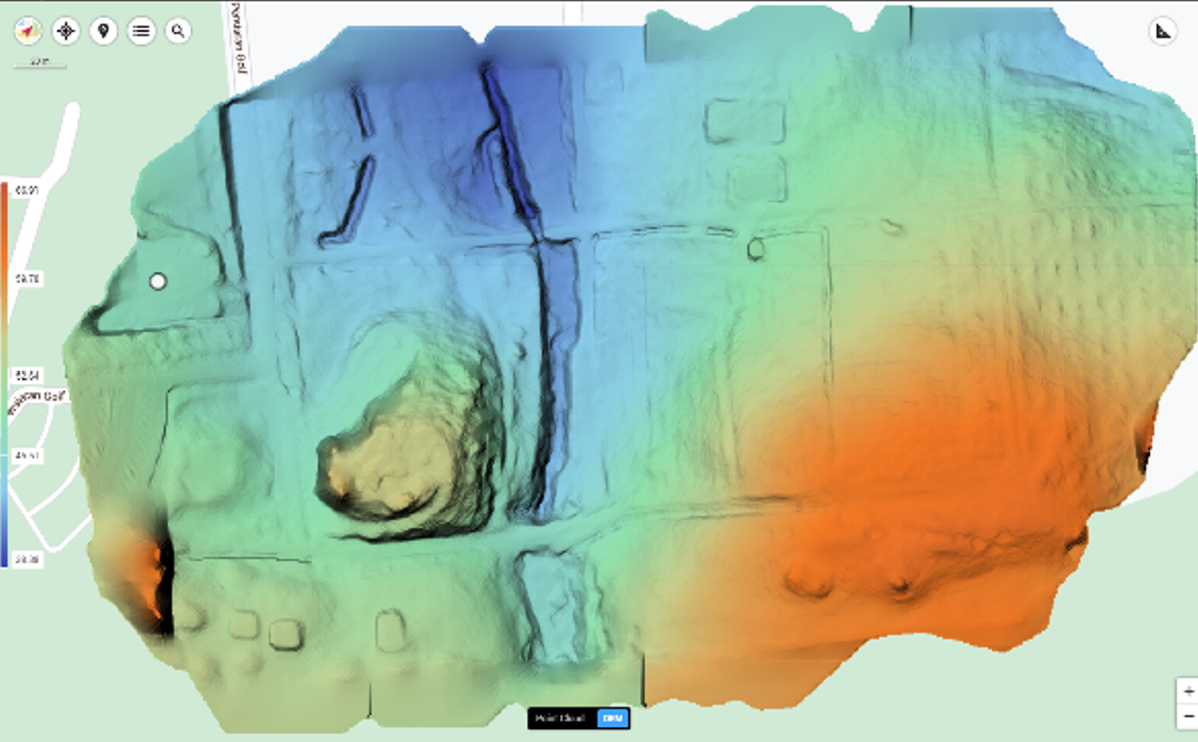
Figure 1: Digital Elevation Models (DEM)
|
- Crop Biomass Estimation - LiDAR is highly effective in estimating crop biomass by capturing detailed crop structure such as height, canopy density, and leaf area index. This data allows for remote, accurate monitoring of plant growth and helps in scheduling optimal fertilization and pest control. When combined with machine learning, LiDAR can further enhance biomass estimation and resource management.
- Yield Prediction and Health Monitoring - LiDAR can predict crop yields and monitor plant health by analyzing canopy structure and volume. Some advanced systems can detect nitrogen levels and chlorophyll content, enabling targeted fertilizer application and early detection of nutrient deficiencies or diseases. This contributes to healthier crops and higher productivity.
Future Potential
As LiDAR technology evolves, its integration with AI and advanced data analytics is expected to improve real-time monitoring and predictive modeling. Future developments aim to reduce costs and make technology more accessible to small and medium-scale farmers.
LiDAR is a game-changer in smart agriculture, supporting sustainable plantation practices, optimizing resource use, and enhancing productivity across the agricultural sector.
|

Figure 2: 3D Models of crops
|
Date of Input: 30/04/2025 | Updated: 26/09/2025 | ainzubaidah
MEDIA SHARING