The fluctuation of petroleum prices, fast depletion of fossil resources and environmental problems are caused by polymer derived from petroleum or natural gas due to its non-renewable and non-biodegradable properties. Recently, the industry has emphasised designing sustainable biocomposite using eco-friendly, renewable, biodegradable and low energy consumption during the manufacturing process. This target can be obtained by producing a mycelium-based composite (MBC) uses the fungal mycelium matrix to bind composite material. The selection of suitable fungi and type of lignocellulosic biomass is essential for good mycelial network development. White-rot fungi have high possibilities of producing mycelium-based composite due to their ability to secrete lignin-degrading enzymes that can degrade lignocellulosic biomass for nutrients uptake. Agricultural waste such as lignocellulosic biomass has a great potential to be converted into the mycelium-based composite. Fungal mycelia act as a natural adhesive or binder that binds together all particles of lignocellulosic biomass during fungal colonisation. The mycelium growing phenomenon is manipulated to produce the mycelium-based composite such as biofoam, paper, textiles, vehicle parts, packaging materials and higher value composite materials. Renewable MBC is a key alternative for non-renewable packaging materials. Along these lines, the MBC serves several advantages as it does not require complex and high-end manufacturing processes, low energy consumption during production, low density, competitive strength, tensile and impact mechanical properties. It also has excellent resistance to corrosion and the possibility of being a sustainable source for a long period. This will pave the way for the mycelium-based composite from lignocellulosic biomass for its use in various applications.

Figure 1

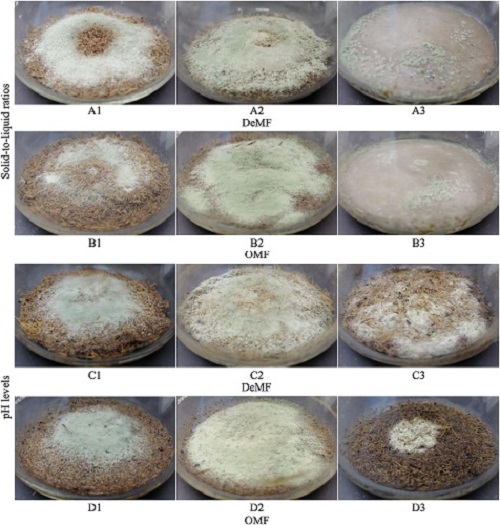
Figure 2
Mariam Jamilah Mohd Fairus., Ezyana Kamal Bahrin., Enis Natasha Noor Arbaain., Norhayati Ramli (2022). Mycelium-based composite: A way forward for renewable material. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management 17(1): 271-280
Tarikh Input: 23/08/2022 | Kemaskini: 17/01/2024 | ainzubaidah
PERKONGSIAN MEDIA